What is § 24 AufenthG?
§ Section 24 of the Residence Act (AufenthG) is a key legal provision that makes it possible to grant temporary protection in Germany to people who are collectively fleeing war and persecution.
In contrast to the individual asylum procedure, which examines individual requirements, Section 24 AufenthG offers protection for groups without the need to prove individual grounds for persecution. The regulation is initially limited to one year, but can be extended if risks persist in the country of origin.
The importance of temporary protection
Temporary protection under Section 24 of the Residence Act plays a crucial role for refugees, especially those from Ukraine, but also for other migrant groups fleeing conflict. It offers immediate security and opens up opportunities for integration into German society. Holders of this protection title can work, take part in integration and language courses and make use of the education system.
This not only facilitates social and professional integration, but also creates prospects for permanent settlement or the acquisition of German citizenship. Section 24 of theResidence Act is therefore a fundamental basis for the protection and new start of migrants in Germany.
Requirements for protection according to § 24 AufenthG
For Ukrainian citizens seeking refuge in Germany from the consequences of the conflict in their home country, the residence permit under Section 24 AufenthG is a crucial option. Understanding the requirements for temporary protection is essential for applicants to successfully apply for and receive protection.
This section highlights the personal requirements that must be met and discusses special circumstances that are taken into account during the application process. Directive 2001/55/EC on temporary protection, which is also set out in Section 24 (1) of the Residence Act, is crucial.
Personal requirements for applicants
In order to be considered for Residence permit in accordance with Section 24 AufenthG, applicants must fulfill various personal requirements:
Nationality: You must be a Ukrainian citizen or have had your habitual residence in Ukraine as a stateless person before the conflict.
Flight: You must prove that you have fled due to the conflict in Ukraine.
Residence in Germany: You are already in Germany or at the border to Germany and apply for protection.
No grounds for exclusion: There are no grounds that justify exclusion from protection under German law or international agreements, such as serious criminal offenses.
Special circumstances that are taken into account
In addition to the personal requirements, there are special circumstances that can be taken into account when applying for temporary protection in accordance with Section 24 AufenthG:
Family status: The presence of family members in Germany can have an influence on the application, especially when it comes to the protection of children.
Health situation: Serious health problems that require special medical care are taken into account.
Vulnerability: Particular need for protection, for example in the case of women traveling alone, children, elderly people or people with disabilities.
Integration in Germany: Previous integration efforts, such as language acquisition or participation in educational measures, can be assessed positively.
The application process for § 24 AufenthG
The application process for temporary protection under Section 24 AufenthG is a crucial step for Ukrainian citizens seeking safety in Germany. In order to make the process as smooth as possible, it is important to understand exactly where and how the application is made, which documents are required and what procedural durations and processing times can be expected.
Where and how to submit the application?
The application for temporary protection in accordance with Section 24 AufenthG can be submitted to the responsible Foreigners' office at your current place of residence in Germany. In some cases, initial reception facilities or special contact points for refugees can also be the first point of contact:
Foreigners' officeThe main contact person for the application . The exact address and opening hours can be found on the website of the respective city or district.
Initial reception centers: For newly arrived refugees, these facilities often provide initial information and support with the application process.
Online forms: Some federal states offer the option of preparing the application online or submitting it completely digitally. Information on this can be found on the websites of the respective immigration authorities.
Documents and information required
Various documents and information are required for the application in order to prove identity and authorization for protection:
Passport or proof of identity: Valid Ukrainian passport or other identity documents.
Proof of residence in Ukraine: documents proving residence in Ukraine before fleeing.
Registration at Foreigners' office: Confirmation of registration, if already done.
Proof of special circumstances: medical documents, birth certificates of children, etc., if applicable.
Procedure duration and processing times
The duration of the procedure for applying for temporary protection under Section 24 AufenthG may vary depending on the current situation and the capacity of the authorities:
Initial assessment: As a rule, an initial assessment of the application is carried out within a few days.
Complete processing: The complete processing and decision can take several weeks to months.
Up-to-date information: It is advisable to regularly enquire about the status of the procedure at Foreigners' office .
Rights and obligations under § 24 AufenthG
For Ukrainian citizens who receive protection in Germany under Section 24 of the Residence Act, there are not only certain rights but also obligations. These regulations are intended to facilitate integration on the one hand and to ensure that those seeking protection comply with the legal requirements in Germany on the other. The key points relating to work, education, healthcare and social services as well as residence requirements and travel restrictions are explained below.
Access to work and education
Under Section 24 of the Residence Act, people seeking protection are granted certain rights that are intended to support their integration into German society and the labor market:
Access to the labor market: Holders of a protection title under § 24 AufenthG can obtain a work permit shortly after arriving in Germany. This makes it easier to enter the labor market quickly.
Access to education: Children and young people have the right to school education. Adults have access to integration courses and, depending on availability, to further vocational training.
Healthcare and social services
Healthcare and access to social services are essential components of protection under Section 24 AufenthG:
Health care: People seeking protection are entitled to medical care, including necessary treatment and medication.
Social services: Counseling services, psychosocial support and assistance in finding housing are available to facilitate integration into German society.
Residence requirements and travel restrictions
The protected status is also associated with certain obligations and restrictions:
Residence requirements: Persons seeking protection may be obliged to live in certain accommodation or in a certain area. Changes of residence require the approval of Foreigners' office.
Travel restrictions: The ability to leave Germany or travel to your home country may be restricted. Before traveling abroad, permission should always be obtained from Foreigners' office so as not to jeopardize the protection status.
Integration and life in Germany
For Ukrainian citizens living in Germany under the protection of Section 24 of the Residence Act, integration is an important step towards a fulfilling and independent life. Integration encompasses various areas, from language support to participation in cultural life. In this context, the fictitious certificate and the role of the Federal Office for Migration and Refugees (BAMF) also play an important role.
Integration courses and language support
Mastering the German language is the key to integration. The BAMF and other institutions offer this:
Integration courses: Combined language and orientation courses that prepare you for life in Germany.
Special language support programs: For children, young people and adults to acquire German language skills quickly and effectively.
Work permit and employment opportunities
The opportunity to work and earn your own income is crucial for integration:
Professional recognition: Advice and support with the recognition of foreign professional qualifications.
Placement and qualification: Programs for vocational training and job placement.
Cultural integration and social participation
Becoming part of social life in Germany requires commitment and support:
Clubs and organizations: Participation in sports, cultural and leisure clubs.
Voluntary work: Involvement in social projects promotes networking and an understanding of German society.
Fictitious certificate
The fictitious certificate is a temporary proof of legal residence status while the application for a residence permit is still being processed:
Bridging: Serves as proof of legal residence until the application for protection under § 24 AufenthG has been finally processed.
Rights: Permits employment and participation in integration courses under certain conditions.
Role of the Federal Office for Migration and Refugees (BAMF)
The BAMF plays a central role in the integration of people seeking protection:
Information and advice: Provides comprehensive information on integration courses, language support and professional integration.
Support services: Coordinates programs for the social, cultural and professional integration of refugees.
Successful integration in Germany is a process that depends both on the individual efforts of those seeking protection and on the support of governmental and non-governmental organizations. By taking advantage of the courses, programs and services on offer, Ukrainian citizens can successfully shape their path to a new life in Germany.

Naturalization according to § 24 with the new Naturalization Act
With the draft law on the modernization of citizenship law (StARModG), the Federal Government aims to simplify and accelerate access to German citizenship in order to enable equal participation for foreigners living permanently in Germany.
However, nothing changes for refugees from Ukraine who are holders of § 24 AufenthG and all holders of § 24 AufenthG. The § 24 AufenthG remains blocked for Naturalization and the Residence permit must be changed!!!
Overview of the new naturalization law
The new Naturalization Act aims to promote a good naturalization culture and create incentives for integration. The key points of the law reform are
Simplification of Naturalization: The minimum period of residence for Naturalization is reduced from eight to five years.
Recognition of integration achievements: Special integration achievements, such as excellent language skills, can lead to a further reduction in the length of stay.
Admission of multiple nationality: The previous principle of avoiding multiple nationality will be abolished, allowing Naturalization without giving up the original nationality.
Requirements for Naturalization under the new law
The requirements for Naturalization under the new law include
Legal residence: A permanent and legal residence in Germany.
Language skills: Proof of German language skills at least at B1 level of the Common European Framework of Reference for Languages.
Livelihood: Proof of being able to support yourself and your family without claiming social benefits.
Application process and required documents
The application process for Naturalization under the new law includes
Naturalization application: Submission of a formal application to the competent naturalization authority.
Required documents: Submission of documents proving residence status, identity, language skills and economic independence.
Challenges and tips for a successful Naturalization
To make the naturalization process successful, applicants should:
Early preparation: Find out about the necessary documents and requirements in good time.
Deepen language skills: Active participation in language courses to improve German language skills.
Use advice services: Use advice centers that can help with the application process.
What will change for holders of Section 24 AufenthG?
For persons who have found protection in Germany under § 24 AufenthG, the new law does not include an easier path to Naturalization. Naturalization is blocked for this Residence permit ! If the Residence permit has been changed and you are in possession of a residence permit in accordance with § 10 StAG, the situation changes.
If the change to the new right of residence has worked out, there is an advantage as a Ukrainian:
Recognition of multiple citizenship: renunciation of Ukrainian citizenship is no longer required, which should make the decision to Naturalization much easier.

Family reunification under § 24 AufenthG
For Ukrainian citizens who are protected in Germany under Section 24 of the Residence Act, family reunification is an important aspect of maintaining family unity and supporting their integration. The right to family reunification makes it possible to reunite separated families and build a new life together in Germany.
Requirements for family reunification
Family reunification is to be granted in deviation from § 5 Para. 1 AufenthG. Therefore, you do not have to provide proof that you have secured accommodation or livelihood. Certain requirements must be met to enable family reunification:
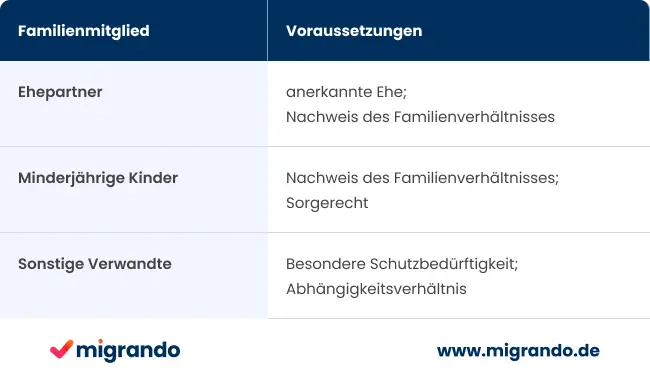
Legal status: The applicant must have a recognized protection status in Germany in accordance with § 24 AufenthG.
Family relationship: There must be a verifiable family relationship with the applicant. As a rule, this is a spouse, unmarried minor children or, in exceptional cases, other family members who are in particular need of protection.
Application procedure for family members
The application procedure for family reunification comprises several steps:
Application: The application for family reunification must be submitted to the German diplomatic mission in the country of origin or, if this is not possible, to Foreigners' office in Germany.
Documents: The following documents are usually required:
Valid passports of family members
Marriage certificate or birth certificates as proof of family circumstances
Visa procedure: After a positive review of the applications by the diplomatic mission abroad, the family members receive a visa for family reunification.
Entry and residence permit: After entering Germany, the family members joining them must apply for a residence permit at the relevant Foreigners' office .
Challenges and support
The procedure for family reunification can be complex and requires careful preparation and submission of the necessary documents. It is recommended to contact advice centers at an early stage, which can offer support during the process. In addition, integration courses and other social integration services can make it easier for family members to start life in Germany.
Extension and termination of protection
While the discussion on the protection of Ukrainian citizens in Germany continues, it is important to consider the specific legal framework that regulates their residence. Section 24 of the Residence Act provides a protection mechanism for people who have fled conflict en masse. However, the situation regarding a ban on deportation under Section 60 (5) AufenthG must be considered specifically for persons from Ukraine.
Criteria for the extension of temporary protection
The extension of temporary protection under Section 24 AufenthG takes into account the persistent circumstances that led to the flight. It should be noted here:
Prohibition of deportation according to § 60 para. 5 AufenthG: There is currently no general ban on deportation for Ukraine, as provided for in Section 60 (5) Residence Act for situations in which people are at risk of serious harm in their country of origin. This underlines the importance of Section 24 of the Residence Act for Ukrainian citizens, as it is specifically geared towards the situation of people fleeing en masse and provides a framework for their protection.
The announcement by the Federal Ministry of the Interior and Homeland in the Federal Law Gazette of November 2023 that the protection status for Ukrainian citizens and their family members who have fled the war in Ukraine has been automatically extended until March 4, 2025, which represents a significant extension and security for those affected, is also crucial.
Termination of protection and return options
The termination of protection and the associated return options must be considered in light of the current regulations:
Situation in Ukraine: An improvement in security and living conditions in Ukraine could theoretically lead to a review and possible revocation of protection status. However, as there is no general ban on deportation under Section 60 (5) AufenthG, protection under Section 24 AufenthG is of particular relevance.
Voluntary return: There are support programs for people who wish to return voluntarily. However, this decision should be made carefully and in consideration of the current situation in Ukraine.
Change of residence title: The possibility of changing to another Residence permit remains an important option for those whose protection status ends and offers the prospect of long-term residence in Germany.
Conclusion and outlook
The legal framework in Germany offers essential support and protection to Ukrainian citizens who have had to flee the conflict in their home country. Section 24 of the Residence Act is a central pillar in guaranteeing this protection and offering those affected a perspective in Germany.
The significance of Section 24 AufenthG for the future
Section 24 of the Residence Act has proven to be a crucial instrument for responding to the dynamic challenges and needs of refugees in times of crisis. For the future, this paragraph underlines the need for flexible and humanitarian approaches in dealing with refugee movements:
Adaptability: Experience with Section 24 AufenthG shows how important it is to have an adaptable legal framework in order to be able to react quickly to crises.
Integration: The integration of people seeking protection remains a key issue. Access to education, work and social services is crucial for successful integration into society.
Solidarity: The protection of refugees is a joint task that requires solidarity and commitment at local, national and international level
FAQ - The most important questions and answers on Sec. 24 AufenthG
The right of residence under Section 24 AufenthG is generally granted for one year initially. An extension is possible and depends on the ongoing risk situation in Ukraine. Applications for extension must be submitted in good time.
With § 24 AufenthG you do not make an application for asylum, you only make an application for asylum. In this case, you will be treated for identification purposes in the form of an initial registration carried out by the BAMF and the immigration authorities and, depending on the capacity of the social welfare offices (distribution according to the Königstein key - utilization and fair distribution around the federal territory), you will receive an allocation decision and thus apply for a Residence permit §24 Residence Act.
There is no automatic extension of the residence permit under § 24 AufenthG. Those affected must actively apply for an extension if the reasons for the original protection still apply. It is important to contact the responsible Foreigners' office in good time before the residence permit expires.
No, persons with protection status under Section 24 AufenthG cannot apply directly to Naturalization . Section 24 AufenthG will also be blocked for Naturalization with the new Naturalization Act. This means that anyone who wants to become a German citizen under Section 24 AufenthG must change their Residence permit and can only then submit the application.
Yes, unaccompanied refugee minors are entitled to protection in Germany under Section 24 of the Residence Act, which grants them temporary protection if they meet the general requirements. They must apply for protection status from the relevant authorities, such as Foreigners' office or a reception center. This group enjoys special protection and support from the Youth Welfare Office, which provides appropriate accommodation and covers their basic needs until a permanent solution is found. In addition, they are given access to education and healthcare to facilitate their integration and the establishment of a new life in Germany.
The protection status according to § 24 AufenthG facilitates family reunification in Germany by enabling persons entitled to protection to join close family members. The prerequisites are proof that you are in possession of § 24 AufenthG and that you have a corresponding situation. Through your Residence permit you do not have to prove that you have sufficient means of subsistence or housing for family reunification. The regulation deviating from § 5 AufenthG applies here
Ukrainian citizens seeking protection in Germany are not subject to a general ban on deportation under Section 60 (5) AufenthG. This paragraph protects people from deportation if they are at risk of serious harm in their country of origin. While the protection status under Section 24 AufenthG offers Ukrainians temporary protection, the lack of a ban on deportation under Section 60 (5) means that each situation is assessed individually and protection is based on legal grounds other than a general ban on deportation. This underlines the importance of a careful examination of each individual case and the search for alternative protection options within German residence law.








